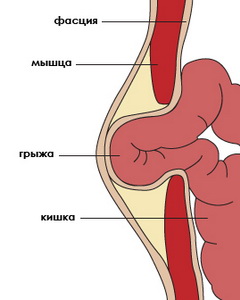
Postoperative hernia abdominal cavity call the situation when surgical intervention in the abdominal cavity leads to the subsequent exit of the gastrointestinal tract (usually the intestines) beyond the peritoneum at the site of the former incision. In the photo it looks like a tumor different size, along which the postoperative scar passes, and it is accompanied primarily by pain. If the inside of the organ is infringed, nausea, gas formation, vomiting and stool instability also appear. To determine such a disease (in addition to a visual examination by a doctor), it is necessary to carry out a number of procedures such as x-rays, herniography, ultrasound and CT of the entire abdominal cavity, including the hernia itself. As a solution to the problem, doctors usually resort to hernioplasty - a surgical operation to suture a hernia.
Causes of the exit of the gastrointestinal tract beyond the peritoneum
Postoperative hernia of the abdominal cavity, which is also called ventral or cicatricial, can form both immediately after surgery and after some time. According to statistics, from seven to ten percent of people who have undergone surgery on the digestive tract subsequently face a similar problem.
At the same time, among all hernias formed in the peritoneum, postoperative ones account for about 20%.
Traditionally, a postoperative hernia is formed where an incision was made by doctors to access the internal organs. As a rule, these are the following places:
- white line of the abdomen due to median laparotomy;
- right iliac zone after removal of the appendix or after surgery on the caecum;
- right or left hypochondrium, depending on the operation - cholecystectomy, liver resection, surgery on the spleen;
- lateral lumbar area due to surgery on the ureters or kidneys;
- suprapubic area after urological or gynecological interventions.
Most often, postoperative hernia of the abdominal cavity becomes the result of operations on the gastrointestinal tract, which were carried out in a hurry without providing all the necessary preparation. internal organs. This almost inevitably leads to negative consequences already after the operation, when pressure rises inside the peritoneum, intestinal masses begin to pass poorly through the intestines, chronic flatulence appears, breathing is depressed and a cough is formed. All these factors, resulting from the general degradation of intestinal motility, lead to negative conditions for scar formation after surgery. There are other reasons associated with the formation of a postoperative hernia, among which the key ones are:
- unsuitable or outdated operating equipment;
- suture material of reduced quality;
- excessive tension of local tissues;
- hematomas, suppuration or inflammation;
- torn seams;
- drainage of the abdominal cavity;
- excessive tamponade during surgery.
 There are also factors directly related to the patient himself: first of all, this is his non-compliance with the regimen, which requires the absence of physical activity after surgery. Secondly, this is a violation of the prescribed diet and non-compliance with the need to use a bandage. Of course, there are also diseases, the presence of which in a patient will have an additional provocative value in the event of the likely formation of a postoperative hernia of the abdominal cavity. Such diseases include pneumonia (or acute bronchitis), constipation, pregnancy (or childbirth), diabetes, obesity, general weakness and vomiting. Another reason can be any disease that is characterized by a destructive effect on the structure of connective tissue in the body.
There are also factors directly related to the patient himself: first of all, this is his non-compliance with the regimen, which requires the absence of physical activity after surgery. Secondly, this is a violation of the prescribed diet and non-compliance with the need to use a bandage. Of course, there are also diseases, the presence of which in a patient will have an additional provocative value in the event of the likely formation of a postoperative hernia of the abdominal cavity. Such diseases include pneumonia (or acute bronchitis), constipation, pregnancy (or childbirth), diabetes, obesity, general weakness and vomiting. Another reason can be any disease that is characterized by a destructive effect on the structure of connective tissue in the body.
Almost any operation performed on the gastrointestinal tract can ultimately lead to the formation of a corresponding hernia, but the most dangerous in this regard are those caused by diseases such as cholecystitis, appendicitis, peritonitis, umbilical hernia, ovarian cysts or uterine fibroids, intestinal obstruction, wounds of the peritoneum, perforated ulcers.
Symptoms of postoperative hernia
It goes without saying that the main symptom that characterizes a postoperative hernia of the abdominal cavity is the tumor-like formation itself, protruding at the site of the surgical suture. Such hernias are very painful and can increase in volume due to physical exertion, attempts, sudden movements. At the same time, when the patient is in a horizontal position, the hernia visually decreases up to the possibility of its reduction (by early stages). If the necessary measures have not been taken, then the pain subsequently becomes stronger, resembling contractions, and the following symptoms also appear:
- bloating and constipation;
- belching and nausea;
- decreased activity;
- dysuric disorders in suprapubic hernias (impaired urination);
- irritation or inflammation skin at the site of the hernia.
It is worth defining those possible complications, in which postoperative hernia of the abdominal cavity can cause additional problems. These doctors include infringement, perforation, adhesive intestinal obstruction, coprostasis (narrowing of the intestinal lumen up to its closure). In situations like this pain the patient increases markedly, and signs such as nausea, vomiting, bloody stools, delayed bowel movements or gas separation may be added to them. In addition, it is no longer possible to correct such a hernia, even if the patient is lying on his back.
Classification of abdominal hernias
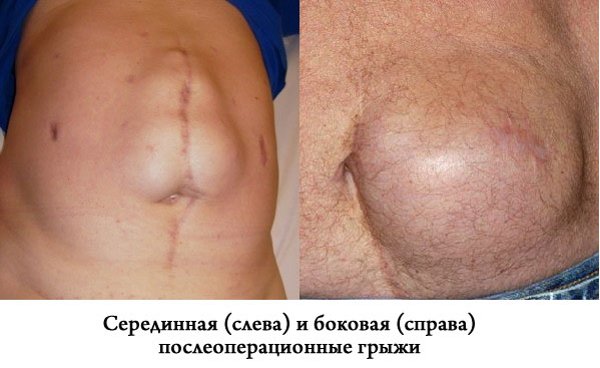 First of all, postoperative abdominal hernias are distinguished by their localization relative to the center of the abdomen: they can be median (upper or lower) and lateral (upper lateral or lower). In addition, they differ in size, divided into small, medium, extensive and giant. These dimensions are characterized as follows:
First of all, postoperative abdominal hernias are distinguished by their localization relative to the center of the abdomen: they can be median (upper or lower) and lateral (upper lateral or lower). In addition, they differ in size, divided into small, medium, extensive and giant. These dimensions are characterized as follows:
- at small, the configuration of the abdomen does not change;
- with medium, a small part of a separate area of \u200b\u200bthe peritoneum is allocated;
- with extensive, the entire separate area of \u200b\u200bthe peritoneum is allocated;
- giant ones occupy from two areas of the peritoneum or more.
Separately, doctors divide incisional hernias into those that can and cannot be reduced, as well as those that contain one chamber or more. All these factors determine the subsequent treatment.
Features of the treatment of this disease
With a postoperative hernia, it may be permissible to use the so-called conservative tactics, but only in the situation of adding any significant contraindications to the surgical intervention. In such situations, it is highly recommended to follow a dietary diet, an absolute rejection of physical activity. It will also be very important to ensure the fight against constipation and not to forget about the constant use of a supporting bandage. However, in any other cases, it is surgical intervention that will be effective so that the postoperative hernia does not provoke the development of complications.
Radical disposal of it can be carried out exclusively by the surgical method, namely with the help of hernioplasty. It is highly recommended to pay attention to the following:
- a specific method of surgical intervention in the presence of a hernia is selected based on the location and size of the protrusion;
- it is very important to take into account the presence of adhesive algorithms between the peritoneal organs and the hernial sac;
- with minor and unaggravated defects after surgery (less than five cm), elementary suturing of the aponeurosis can be performed. This is about plastic surgery in relation to the anterior wall of the peritoneum due to the local tissue cover;
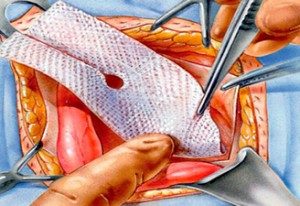
- medium, extensive, gigantic, long-term and aggravated hernias after surgery need to hide the defect of the aponeurosis with the help of the so-called synthetic prosthesis. We are talking about hernioplasty with the introduction of a mesh prosthesis.
 In the latter case, various methods of equipping the mesh system in relation to the physiological structures of the peritoneum can be applied. In such situations, separation of adhesions or dissection of scars is expected. In addition, when such a hernia is infringed, resection of the intestine and omentum is recommended. In order for postoperative hernia not to be associated with complications, certain preventive measures are necessary.
In the latter case, various methods of equipping the mesh system in relation to the physiological structures of the peritoneum can be applied. In such situations, separation of adhesions or dissection of scars is expected. In addition, when such a hernia is infringed, resection of the intestine and omentum is recommended. In order for postoperative hernia not to be associated with complications, certain preventive measures are necessary.
What are the preventive measures?
Prevention of hernias after surgery requires the specialist to choose an exceptionally correct and physiological access for any type of intervention. It will be very important to observe scrupulous asepsis at each stage of the operation. We should not forget about the use of high quality material for suturing, adequate preparation before surgery and management of the patient after such an intervention.
At the stage after the operation, it will be necessary for the patient to strictly comply with all recommendations in terms of nutrition and the mandatory wearing of a bandage. Of course, it will be very important to remember about physical activity, weight stabilization, limitation of physical activity (exclusion of intense effort), regularity in emptying the bowel area. Such measures may seem elementary, but it is they that allow in the future to avoid such an undesirable consequence as a postoperative hernia.
Hernia prognosis
Hernias after surgery, even if there are no complications, lead to aggravation of physical and labor activity. In addition, the list of consequences includes cosmetic defects, a significant deterioration in the quality of life. According to experts, infringement of a hernia after surgery quite often (in about 8.8% of cases) provokes a lethal outcome. After the surgical elimination of such a phenomenon as a postoperative hernia (with the exception of situations with multiple relapses), the prognosis is satisfactory.
Important!
HOW TO SIGNIFICANTLY REDUCE THE RISK OF CANCER?
Time limit: 0
Navigation (job numbers only)
0 of 9 tasks completed
Information
TAKE A FREE TEST! Thanks to the detailed answers to all questions at the end of the test, you will be able to REDUCE the likelihood of getting sick at times!
You have already taken the test before. You cannot run it again.
Test is loading...
You must login or register in order to start the test.
You must complete the following tests to start this one:
results
Time is over
1. Can cancer be prevented?
The occurrence of a disease such as cancer depends on many factors. No one can be completely safe. But significantly reduce the chances of occurrence malignant tumor everyone can.
2. How does smoking affect the development of cancer?
Absolutely, categorically ban yourself from smoking. This truth is already tired of everyone. But quitting smoking reduces the risk of developing all types of cancer. Smoking is associated with 30% of deaths from oncological diseases. In Russia, lung tumors kill more people than tumors of all other organs.
Eliminating tobacco from your life is the best prevention. Even if you smoke not a pack a day, but only half, the risk of lung cancer is already reduced by 27%, as the American Medical Association found.
3. Does it affect excess weight to the development of cancer?
Keep your eyes on the scales! Overweight affect not only the waist. The American Institute for Cancer Research has found that obesity contributes to the development of tumors in the esophagus, kidneys, and gallbladder. The fact is that adipose tissue serves not only to store energy reserves, it also has a secretory function: fat produces proteins that affect the development of a chronic inflammatory process in the body. And oncological diseases just appear against the background of inflammation. In Russia, 26% of all cancer cases are associated with obesity.
4. Does exercise help reduce the risk of cancer?
Set aside at least half an hour a week for exercise. Sport is on the same level as proper nutrition when it comes to cancer prevention. In the US, a third of all deaths are attributed to the fact that patients did not follow any diet and did not pay attention to physical education. The American Cancer Society recommends exercising 150 minutes a week at a moderate pace or half as much but more vigorously. However, a study published in the journal Nutrition and Cancer in 2010 proves that even 30 minutes is enough to reduce the risk of breast cancer (which affects one in eight women in the world) by 35%.
Postoperative hernia, or cicatricial, occurs when the organs of the peritoneum (intestine, greater omentum) protrude beyond abdominal wall in the scar part, which was formed after surgery. A postoperative hernia of the abdomen is manifested by a protrusion in the area of the postoperative scar, which becomes less noticeable or disappears altogether when a person takes a supine position.
This condition must be treated by a surgeon. If after the operation the patient felt inconvenience or discomfort in the area of the scar, it is necessary to notify the doctor about this.
In postoperative hernia, the symptoms are as follows:
- protrusion in the area of the scar similar to a tumor;
- the occurrence of nausea and vomiting, as well as bloating;
- the occurrence of pain during movement or muscle tension;
- soreness in the scar.
Classification of pathology
Doctors classify hernias after surgery according to various parameters, namely:
- By size. They can be gigantic when multiple hernias form. At the same time, the human stomach is too deformed. Extensive hernias protrude on one side, can deform the walls of the peritoneum. Medium hernias of small size, slight protrusion. And small hernias are almost imperceptible, they are usually found by chance during palpation of the abdominal walls.
- By location, a postoperative ventral hernia can be located on the side, in the middle of the abdomen, or be mid-lateral.
- By origin. Hernias can be congenital or acquired over time.
- By the presence of complications. They can be complex or uncomplicated.
- According to the course of the disease, they are divided into primary, recurrent or postoperative.
- By correctness. Hernias that can be reduced or not amenable to reduction.
Causes and diagnosis
 Postoperative hernia of the abdominal cavity can develop after the following surgical interventions:
Postoperative hernia of the abdominal cavity can develop after the following surgical interventions:
- after removal of the appendix;
- after laparoscopy;
- after surgery on the ureters;
- after intestinal obstruction;
- after peptic ulcer surgery;
- if the gallbladder is removed;
- after liver resection;
- after gynecological operations, such as removal of the uterus.
A hernia of the abdomen after the operation may occur for the following reasons:
- hereditary predisposition. If the patient has a systemic weakness of the connective tissue, then the possibility that a hernia on the abdomen will develop after the operation is very high. There are a number of signs that indicate this: high growth, asthenic physique, the skin is thin and easily stretchable, the presence of hernias in other places, hypermobility of the joints.
- Violations that occurred during the healing of the scar. If an infection has got into the wound, then it suppurates. As a result, the scar becomes less durable. In addition, there are cases when there is a rejection of the suture material, the edges of the wound at the same time, not having time to grow together, will disperse.
- Non-compliance with the regimen prescribed by the doctor. This means that the patient did not follow the doctor's instructions for a gentle regimen after the operation. Frequent mistakes of patients are that they believe that the wound is only on the outer part of the abdomen, forgetting about the internal wound. If the external wound heals on average in 2 weeks, then the aponeuric scar heals much later, on average 3-4 months, and in the elderly this period is 6-7 months. Therefore, in order to avoid the development of a postoperative hernia, it is necessary to listen and follow the recommendations of the doctor and wear a protective bandage for the right amount of time.
- Associated diseases. These are mainly those ailments that increase intra-abdominal pressure. For example, chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma, constipation, prostate adenoma, obesity and many others.
- Technical violations at the time of wound closure. This reason is extremely rare. A hernia can form due to strong or, conversely, weak tension of the edges of the wound.
As a rule, diagnosing postoperative hernias in the abdominal cavity is not difficult. There are some difficulties if the patient is overweight. In this case, auxiliary diagnostics is necessary: ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, MRI or computed x-ray tomography.
Reasons why you should treat an incisional hernia
The appearance of a hernia indicates that the internal organs have changed their location and can put pressure on each other, leading to dysfunction of each organ. The first sign of a postoperative hernia may be constipation, which ultimately leads to general intoxication of the body, and this disrupts the work of everything. gastrointestinal tract.
Left untreated, this condition will eventually lead to a number of serious complications:
- Caprostasis. This is a peritoneal stagnation of feces in the large intestine.
- The hernial sac becomes inflamed, that is, the organs in it.
- Infringement of a hernia. In the hernial orifice, a sudden squeezing of the contents of the hernia begins. As a result, the blood supply to the organs is disrupted in the hernial sac, which leads to tissue necrosis, and this threatens the death of the patient.
Treatment of ventral hernia
In case of postoperative hernia of the abdominal cavity, the treatment is only surgical. It can be removed as follows:
- Plastic tissue local application. There is a suturing of violations of the aponeurosis of the anterior wall of the peritoneum. Plasty with local tissues is possible only when the hernia is small, that is, less than 5 cm. Removal of the postoperative hernia in this case is performed under local anesthesia, with large hernias, the operation is performed under general anesthesia.
- Plastic with the use of synthetic prostheses, that is, when an aponeurosis defect is covered with synthetic prostheses. The establishment of a protective mesh depends on the location of the hernia. Doctors say that in this case, the likelihood of relapse is minimized. All operations of the surgeon are carried out under general anesthesia.
How to avoid surgery?
 Treatment of a postoperative hernia without surgery is possible if the threat of hernia formation is recognized in time. You must immediately consult a doctor. In this case, for preventive purposes, the doctor may prescribe simple gymnastic exercises, compliance proper nutrition, restorative procedures, the use of a bandage and the restriction of lifting heavy objects.
Treatment of a postoperative hernia without surgery is possible if the threat of hernia formation is recognized in time. You must immediately consult a doctor. In this case, for preventive purposes, the doctor may prescribe simple gymnastic exercises, compliance proper nutrition, restorative procedures, the use of a bandage and the restriction of lifting heavy objects.
Treatment without surgery involves the following steps:
- The bandage is an elastic elastic bandage, thanks to which the internal organs are maintained in a natural state. Wearing a bandage is not necessary, but this way you can protect yourself from infringement, displacement of internal organs, pressure on the affected area, lowering the pain threshold. For preventive purposes, a bandage bandage is also used, but the doctor must select the size so that it does not harm the patient.
- If you have undergone abdominal surgery, then there is no need for a strict diet. But it’s also impossible to eat everything without restriction. Initially, limit carbohydrates and any heavy food. Fresh fruits and vegetables should be on the table every day. Thanks to them, the patient will not suffer from constipation, which is so dangerous in the postoperative period.
Special exercises after surgery are performed only as prescribed by the doctor and under his control. After 3 months, light loads are acceptable, the only restriction will be exercises with sudden movements and weight lifting. Physical exercise improves immune system, because even a simple rhinitis can provoke the recurrence of a hernia.
Surgical intervention, even the most, at first glance, not significant, is stress for the body and after it a certain period of recovery is required. Surgery to remove a hernia is very common, as many people turn to surgeons to get rid of this ailment.
After the doctor has carried out all the necessary procedures, you will be able to return home very soon and begin the recovery period after the operation. That is why you should know the recommendations and rules so that this process is as quick and painless as possible.
Consequences after hernia removal surgery.
Before you go home after surgery, the hospital staff must make sure you can move freely, eat and drink, and go to the toilet on your own.
Do not be afraid if the consequences of the operation to remove the hernia will appear as a slight discomfort in the area of the postoperative scar, this is normal. Doctors will simply prescribe an anesthetic, and the scar itself can be closed with a bandage, and you can easily restore strength and gradually return to a normal, full life.
In the first days of the recovery period, you may experience some of the consequences of a hernia, or rather, the consequences of an operation to remove it. You may experience:
- Discoloration and slight swelling of the skin near the postoperative scar;
- Small bruises may appear;
- There will be numbness or vice versa, sensitivity.
Do not be afraid of such symptoms - all this is the norm, which characterizes the initial stage of the postoperative period.

A hernia after surgery has contraindications and some precautions. Doctors do not recommend driving a car in the first 48 hours after the operation, as the effects of anesthesia can still affect the body, which affects the concentration, coordination and reaction of a person.
Driving a car can cause some tension in the scar that remains after the operation, therefore, in most cases, the doctor will recommend that you stop this activity in the first days of recovery. Also, you will not be able to drive a car and operate other similar mechanisms if you take painkillers.
A hernia in the postoperative period requires certain precautions. You should be very careful when taking a shower and bath. The scar, within a few days after the operation, can not be wetted.
Need to be given Special attention your diet, it should contain foods rich in fiber, you need to drink plenty of fluids: water or fruit juices. This will help to avoid constipation, because overexertion will adversely affect healing and recovery.
Recovery after laparoscopy.
A removed hernia after laparoscopy heals much faster, because instead of one large incision, with the help of this technique, there are severalsmall punctures, the healing of which is much faster and less painful. In this case, the patient is discharged much earlier, and recovery is much faster.
Rehabilitation after surgery to remove a hernia.
When the first and most unpleasant days of the operation are behind you, you should carefully follow the doctor's recommendations regarding the necessary period of time that is necessary to return to a normal, familiar life.
Discomfort and pain intensity will depend on the type of surgery, the location of the removed hernia, and your level of pain tolerance. But in any case, discomfort and slight pain will be present and should not be feared.
The first couple of days after surgery are characterized by discomfort when walking, climbing or descending stairs will also cause difficulty.
The duration of the recovery period will directly depend on your type of activity, it can take from one to six weeks. Your return to work depends on who you are by profession and what duties you perform.
If the work requires significant physical effort associated with lifting and carrying heavy loads or a large number of movements, then, nevertheless, several weeks should be allocated for recovery, after consulting with your doctor. Well, if you are a person of mental labor, then you can return to your workplace in a few days.
Therapeutic exercise to improve recovery.

To improve blood circulation, and thereby speed up the healing process, doctors recommend performing physical exercise with medium or moderate intensity. The best of which is walking.
Sports activities after hernia repair involving heavy lifting or high aerobic activity should be avoided for 6-8 weeks.
For those who play sports intensively or professionally, doctors advise to postpone these activities for several weeks, as this can disrupt the healing and recovery process.
Diet after hernia surgery.
The importance of nutrition after such an operation has already been mentioned above, so it’s worth specifying what you can eat and what you can’t.
It is not recommended to eat those foods that can cause excessive gas formation, bloating and constipation. These foods include: fatty meats, legumes, mushrooms, smoked or spicy foods, pastries, and rye bread. It is not recommended to drink carbonated drinks, kvass, beer, alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks.
Before the stitches are removed, the patient should eat liquid or semi-liquid food: broth, soups, semi-liquid cereals, mashed potatoes, boiled lean meat and fish, and eat foods containing sufficient fiber.
After the stitches are removed, you can return to your usual diet, but gradually and taking into account the recommendations of the doctor.
Article author: Nadezhda Nikolaevna
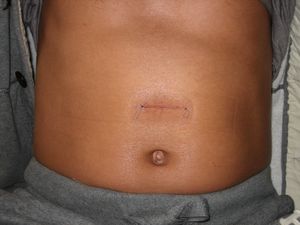 Postoperative hernias (ventral) are lipomas that are localized at the location of postoperative scars. Such bulges, photos of which can be seen in medical reference books, can sometimes appear at a slight distance from the surgical suture. This is due to the fact that the course of the hernia can be bent and accordingly change its direction.
Postoperative hernias (ventral) are lipomas that are localized at the location of postoperative scars. Such bulges, photos of which can be seen in medical reference books, can sometimes appear at a slight distance from the surgical suture. This is due to the fact that the course of the hernia can be bent and accordingly change its direction.
Classification of postoperative abdominal hernia
Specialists from different countries world, in the diagnosis of postoperative hernias, use a single classification (according to the location of the lipoma):
- Lateral hernia - indicated by the letter "L".
- Median hernia - denoted by the letter "M".
- Mid-lateral - denoted by the letters "ML".
When diagnosing such hernias, surgeons take into account the mandatory parameters:
- protrusion size;
- localization of the lipoma;
- hernia gate size, etc.
Modern medicine defines several types of postoperative hernias:
- extensive (they are large and can deform the walls of the peritoneum);
- giant (postoperative hernia, which can protrude in several places at once and severely deform the patient's peritoneum);
- small (a hernia can be detected by palpation or hardware examination, since it is practically not noticeable);
- medium (represent a small protrusion that can be detected during examination).
signs
 The main sign of the appearance of a postoperative hernia is a protrusion, which sometimes causes pain in the patient. On the initial stage the development of a lipoma, when it can be eliminated in a non-surgical way, the patient may not notice any changes in his state of health.
The main sign of the appearance of a postoperative hernia is a protrusion, which sometimes causes pain in the patient. On the initial stage the development of a lipoma, when it can be eliminated in a non-surgical way, the patient may not notice any changes in his state of health.
That is why this disease is often diagnosed too late, when there is no way to do without surgical intervention.
Symptoms
With the appearance of an irreducible postoperative hernia, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- neoplasm, the location of which is the postoperative suture;
- pain, which can intensify even with little physical effort;
- nausea;
- belching;
- vomiting reflex;
- intestinal obstruction;
- flatulence;
- blood in the stool;
- deterioration in general well-being;
- weakness, lethargy, loss of strength, etc.
It is possible to identify the probable infringement of a postoperative hernia by the main symptoms:
- the hernial sac, with any effort, cannot return to the abdominal cavity;
- when pressing on the bulge, the patient experiences pain;
- the temperature may rise slightly;
- dizziness and weakness.
Causes
![]() Modern medicine has identified the main causes of postoperative scarring, which include the following:
Modern medicine has identified the main causes of postoperative scarring, which include the following:
- any form of obesity;
- suppuration of the wound formed as a result of surgical intervention;
- strong physical load on the abdominal region, in postoperative period (persistent cough, lifting weights, etc.);
- atrophy of the muscle tissues of the abdominal cavity;
- defects made by medical personnel when suturing a wound (during surgical removal of hernias);
- any postoperative complications etc.
Complications
Patients who have been diagnosed with an incisional hernia may experience certain complications:
- stagnation of feces (in the large intestine);
- development of inflammatory processes;
- trauma to nearby internal organs, some of which are in the hernial sac;
- infringement of a hernia;
- peritonitis, which can lead to death.
The most dangerous complication that occurs against the background of the development of a postoperative hernia is the infringement of its sac. When squeezing the contents of the lipoma in the hernial orifice, the blood supply is disturbed, which can lead to necrosis of the surrounding tissues. Without proper medical attention, a patient can develop peritonitis within a few hours, which is a deadly threat to the body.
Having identified the symptoms of a strangulated postoperative hernia in a patient, or signs of peritonitis, it is necessary to urgently transport him to the nearest hospital. medical institution, which has a surgical department. emergency surgery will save the life of the patient and allow him to return to his usual way of life after a few weeks.
Diagnostics
If a postoperative hernia is suspected, the patient undergoes a comprehensive examination and, without fail, hardware diagnostics is prescribed:
- ultrasound examination;
- radiography;
- herniography;
- gastroscopy;
- computed tomography, etc.
The surgeon carefully examines the patient, palpates the abdominal cavity. During the examination, he tries to set the protrusion inside the abdominal cavity.
If a lipoma is detected at the initial stage of development, then its non-surgical treatment (reduction) is possible. When a patient applied for medical care in the presence of a strong protrusion, then for him the only method of treating a postoperative hernia will be surgical intervention.
Treatment
 In the surgical treatment of postoperative hernias, specialists perform both a laparotomy (the abdominal cavity is cut) and a more gentle manipulation - laparoscopy. During the surgical intervention, patients undergo hernioplasty, in which the hernia sac is removed and the hernia ring is plas- ticized. In parallel, the contents of the hernia are immersed in the abdominal cavity, and all weak points are strengthened with special artificial (they are used only in the medical industry), or natural materials.
In the surgical treatment of postoperative hernias, specialists perform both a laparotomy (the abdominal cavity is cut) and a more gentle manipulation - laparoscopy. During the surgical intervention, patients undergo hernioplasty, in which the hernia sac is removed and the hernia ring is plas- ticized. In parallel, the contents of the hernia are immersed in the abdominal cavity, and all weak points are strengthened with special artificial (they are used only in the medical industry), or natural materials.
The use of synthetic materials (mesh) during surgery can significantly reduce the number of relapses of this disease. This material works very well in human body, and its presence does not cause any side effects in patients. Within six months, after the surgical removal of the postoperative hernia, the artificial mesh completely grows into the patient's tissues.
Thanks to such a strong frame, patients go through rehabilitation very quickly, go to work and begin to lead an active lifestyle.
In the surgical treatment of postoperative hernias, which are small in size, specialists use the patient's tissue for plastic surgery. In this case, the patient can undergo a simple operation, during which he is given local anesthesia. If the patient is in a state of pregnancy, then she will be prohibited from surgery. Exacerbated chronic diseases that require long-term therapy may also become a contraindication to surgery.
- medical preparations;
- wearing special underwear;
- lack of physical activity.
Prevention
After surgical removal of hernias, patients need to perform the prevention of this disease: 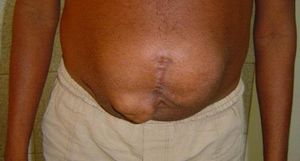
- treat the scar regularly (use only sterile materials and wash hands thoroughly before bandaging);
- avoid sudden movements;
- do not lift weights;
- avoid hypothermia and drafts, which can cause coughing;
- monitor your diet (do not eat foods that cause gas and constipation).
The cost of services in Russian medical centers
To date, in various clinics in Russia, surgery postoperative hernias. Each medical institution independently determines its accounting policy and individually sets prices for surgical procedures.
SHARE WITH OTHERS IF YOU LIKE THIS ARTICLEPostoperative hernia is formed at the site of the surgical scar and is characterized by the exit of the abdominal organs beyond the peritoneum. Often, the greater omentum or bowel loops protrude.
Postoperative hernia tends to grow, under the influence of intra-abdominal pressure, the muscles at the site of the scar can diverge, thereby increasing the hernial orifice. The disease does not drug treatment, surgical intervention is required to eliminate the hernia.
Classification of incisional hernias
In medicine, there are several classifications of incisional hernias, which are divided depending on their scale and location.
According to anatomical and topographic characteristics:
- medial (there are median, lower median and upper median);
- lateral (lower lateral, upper lateral, left-sided and right-sided).
By size:
- small (do not change the shape of the abdomen);
- medium (occupy some part of a separate area of \u200b\u200bthe abdominal wall);
- extensive (located in a separate area of the abdominal wall);
- giant (located in two or three areas).
In addition, small postoperative hernias can be reduced, large protrusions are considered non-right, divided into single and multi-chamber. Specialists single out recurrent hernias as a separate type and repeatedly recurrent ones (they can occur in the same place several times).
Causes of postoperative hernias
1 Emergency operations, where there is no time left for preparing the patient and conducting a comprehensive examination. The patient may experience disruption of the intestines, bloating, stagnation of feces. As a result of this, strong pressure is formed on the abdominal cavity, the healing of the suture and the formation of a postoperative scar takes place with pathologies. 2 Violation of the postoperative regime. Often the patient himself becomes the culprit in the formation of a hernia. Improper nutrition, metabolic disorders, physical activity can lead to a divergence of the abdominal muscle tissue. 3 Inflammatory processes and infectious diseases. After the operation, the human body is weakened and unable to fight the infection. The danger is bronchitis, pneumonia, diabetes mellitus. Constipation, vomiting, fever also adversely affect the healing of the suture. 4 Low quality of operating equipment and human factor. The use of low-quality threads during the operation, strong tissue tension, hematomas and negligence of doctors can cause suppuration and inflammation of the scar. 5 Pregnancy and childbirth. Pregnancy after undergoing surgery on the abdominal organs can provoke tissue divergence. The growth of the fetus increases the pressure on the abdominal muscles, and attempts during the birth process can cause a hernia to bulge.Video
Characteristics of postoperative hernia and features of its treatment.
Symptoms
The first stages of development of a postoperative hernia are practically invisible, the patient may not feel pain, there is no discomfort in the area of the scar. As it grows, the hernial protrusion makes itself felt with the following symptoms:
- neoplasm along the scar line or near it, constantly increasing in size;
- general weakness of the body, constipation, flatulence, nausea, vomiting, belching;
- at the site of the hernia, the skin may become bluish in color.
Ignoring the first signs of a postoperative hernia can lead to its infringement. The advanced stage of the disease is accompanied by urological disorders, stool retention and increasing pain in the abdomen.
Without timely seeking medical help, the patient's condition deteriorates significantly. Possible necrosis of internal organs, intoxication and even death.
Diagnosis of the disease
Hernial formation can be seen visually, the bulge in the area of the postoperative scar is hidden when a person lies, and protrudes when coughing and straining. Very often, patients perceive the protrusion as a cosmetic defect and are in no hurry to see a doctor.
Examination and consultation with the surgeon will help to make an accurate diagnosis. For a more detailed study of the protrusion, the patient should do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. During ultrasonic diagnostics, the doctor will be able to see the size of the cicatricial hernia, its shape, the presence of adhesive processes and changes in the muscular-aponeurotic structures of the peritoneum.
The general condition of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract will be shown by radiography of the stomach and abdominal cavity, the passage of barium through the intestines, herniography and irrigoscopy. The final stage of diagnosis is an MRI of the peritoneum, after which the doctor will be able to choose the optimal method of treatment and removal of the hernia.
Treatment of a hernia on a postoperative scar
In the vast majority of cases, the treatment of postoperative hernia involves surgical intervention. Removal of a hernia occurs with the help of hernioplasty. Small hernial formations up to five centimeters in size are easily eliminated by suturing the aponeurosis. In this case, the plastic of the abdominal wall tissues is closed with local tissues.
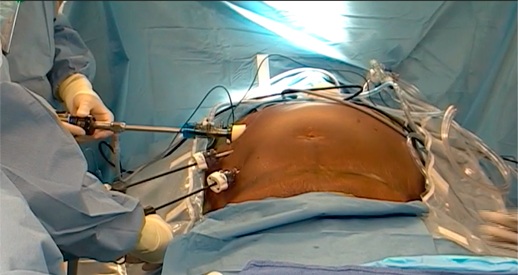
Large hernias, accompanied by complications of the gastrointestinal tract, are closed with a synthetic mesh. In the presence of adhesions and scars, they are dissected, and then only the plastic of the abdominal walls.
In case of infringement of a postoperative hernia, a resection of the omentum and intestine is performed.
Rehabilitation after surgery
After the operation to remove the hernia on the postoperative scar, the patient needs a long rehabilitation period. There are a number of prohibitions, non-observance of which can lead to the recurrence of the protrusion.
The first time, approximately a month and a half, the patient must wear a bandage. It will reduce the pressure on the walls of the abdominal cavity and prevent the divergence of the connective tissues.
The belt should be tightly fixed in place of the scar, but without squeezing it. The period of stay in the belt should be clearly regulated with the attending physician. Often it is worn during the period of exercise, for example, therapeutic exercises or household chores. Before going to bed, the bandage is removed so that the muscles can “rest”.
Physical exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles
Performing simple physical exercises daily, you can not only strengthen the walls of the abdominal cavity, but also bring your body into perfect shape. Gymnastics classes should be started no earlier than one and a half to two months after the operation. Even if the patient is on the mend and does not feel unwell, there is no need to rush things. You need to start with light exercises, leg swings, raising the body. Gradually, you can increase the load, be sure to consult a doctor.
- Lie on your back, legs straight, arms extended along the body. Without bending, raise your legs, changing their order.
- Lying on your back, put on an elastic bandage around your ankles. Take a deep breath, exhaling, raise your legs and stretch the bandage, spread them apart.
- Lying spread your legs shoulder-width apart and grab a small ball with them. Raise and hold for about 30 seconds.
- Sitting on a chair, keep your legs together, hands at your sides. Take a deep breath, exhaling - take the straight leg to the side and back. Repeat with the other leg.
- Ten minute walk. Two steps - inhale, four steps - exhale. While inhaling, turn the torso in different directions.
- The number of approaches to start is minimal, you should monitor your well-being. You can not out of breath, rush, perform too sudden movements. If you feel tired, it is better to take a break and rest a little.
Diet
Nutrition of postoperative patients should be fractional with a predominance of liquid food. You can not overload the stomach and allow stagnation of food. You should completely eliminate foods that contribute to bloating, constipation, or vice versa, can cause diarrhea.
 Mushrooms, fatty meat, legumes, carbonated drinks, hard cereals, fried, smoked, flour are categorically contraindicated. Fruit and vegetable juices, strong tea and coffee, cocoa, milk, alcohol.
Mushrooms, fatty meat, legumes, carbonated drinks, hard cereals, fried, smoked, flour are categorically contraindicated. Fruit and vegetable juices, strong tea and coffee, cocoa, milk, alcohol.
You need to cook for a couple, without the use of hot spices, sauces. In the postoperative period, it is useful to eat soups, porridge on the water, food processed in a blender.
Prevention
Any surgical manipulations do not pass without a trace for the body. During the recovery period, you need to be scrupulous about your own health and follow the prescriptions of doctors. Care must be taken to:
- seam hygiene;
- nutrition;
- avoid physical labor and heavy lifting.
Given that healthy lifestyle life and a sparing regime, the body will quickly recover.
Postoperative hernia is a disease that in most cases occurs due to violations of the rehabilitation regimen and insufficient qualifications of doctors. Only a small percentage of all cases of hernia are due to the patient's predisposition to poor wound healing and weak immunity. Timely treatment will allow you to permanently get rid of hernias.
