In contact with
Classmates
Intrauterine device- a small device made of plastic with elements of copper or metal. It can prevent the onset unwanted pregnancy, reduce this probability to a minimum of a few tenths of a percent.
The essence of its action is the difficulty in the movement of spermatozoa to the egg, reducing the life of the latter and making it impossible for the zygote to attach to the walls of the uterus. To effectively perform these tasks, intrauterine devices for women contain not only copper, but also silver, as a result of which the possibility of internal unwanted infection is reduced.
The intrauterine device in most cases is created in a T-shape, which does not allow the walls of the uterus to touch. The copper base of the spiral installed inside the uterus naturally triggers a local process of inflammation, which affects the reproductive ability of the seminal fluid, significantly reduces it.
Types of intrauterine devices
There are several types of intrauterine contraceptive structures, each of them is endowed with a number of significant advantages, which does not eliminate the presence of certain disadvantages. Choosing an intrauterine device should be guided by the recommendations of your own attending gynecologist, and not by the opinions on dubious forums or girlfriends, whose intimate health can vary significantly. The specialist will select the optimal type of spiral, based on the results of an individual examination of the patient. According to the form of the IUD can be divided into three categories:
- in the form of an anchor (common T-shaped element);
- in the form of a circle;
- in the form of the spiral or loop itself (the least popular, outdated models).
The intensive frequency of using the anchor coil is explained by the fact that this form provides the best reliable location of the foreign body inside the uterus, minimizes the risk of rejection of the coil during active physical exertion or heavy menstrual flow. This phenomenon is called expulsion.
Annular spirals are the most common in China, they are of low cost. An obvious plus is the absence of a threat of deformation of the uterus, its mechanical damage. Serious disadvantages are the probable spontaneous expulsion and the threat of inflammation at the points of contact with body tissues.
The main types of intrauterine devices
The criterion for the main division of the IUD into groups was the composition and device of the element, as a result of which they are characterized as:
- non-hormonal (inert);
- hormonal (medication).
The first type is considered outdated. The first such models were created back in the days of the USSR, now and then they demonstrate low performance and an impressive list of shortcomings leading to serious complications. Some specific coils have been banned from use and manufacture at the WHO level (Lipps loop). Despite the low price and long period of action (up to five years), non-hormonal coils often provoke the development of pregnancy outside the uterus and are not able to protect against the penetration of pathogenic bacteria: they violate the integrity of the mucous barrier at the entrance to the uterus.
Hormonal IUDs are progressive and expensive devices, the creation of which often involves the use of expensive materials - gold, silver, platinum, etc. However, natural components cannot cause fatal harm to the internal microflora female body. The arcs of such a spiral can be straight or curved, each has a miniature container at the base, from which hormones are gradually released, which are normally produced in the ovaries. In the old models - progesterone, in the newest - levonorgestrel. In this case, there are no grounds for the appearance of an ectopic pregnancy, growth and exit of the inner layers of the uterus. The latter may be accompanied by a complete cessation of menstruation.
Insertion and removal of the intrauterine device
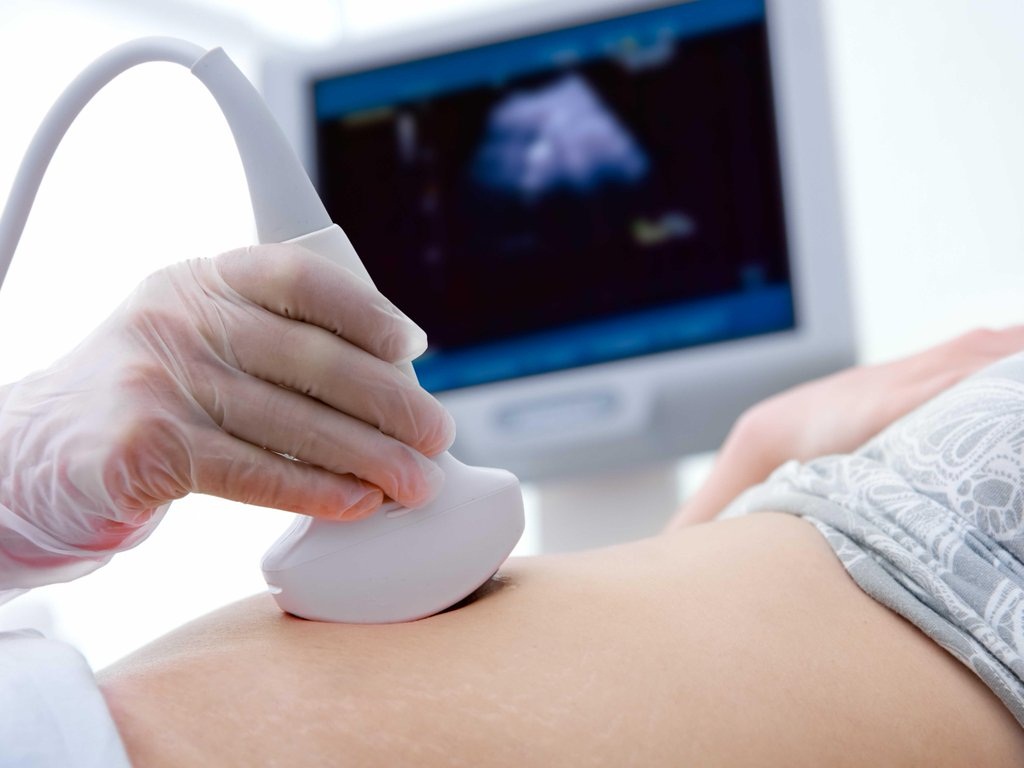
The introduction and removal of the spiral is not accompanied by painful sensations and has a simple mechanism. The process is preceded without fail by an examination by a gynecologist, including an ultrasound scan and an analysis of existing tumors in the genital area or a predisposition to them. If during the examination the presence of pregnancy, any infections, sexual diseases was revealed, the installation of a spiral for a woman is impossible. Any existing inflammation is considered a contraindication.
The optimal time for the introduction of the spiral is the first week of the menstrual cycle, but this does not negate the possibility of installing the IUD on any other day. The first 7 days are the time when you can not be afraid of the presence of an already fertilized egg, and the likelihood of rejection of the spiral is minimized. The IUD has reason to be considered as a means emergency contraception. If the installation of the spiral occurred in a timely manner (within five days after unprotected sexual contact), then the spiral will not allow the zygote to strengthen and develop.
The process of installing the coil lasts a very short period of time, does not involve the work of an anesthesiologist. Women who have managed to give birth to a child usually do not experience any tangible inconvenience, nulliparous patients are able to notice only minor discomfort, its degree is largely determined by the professionalism of the doctor. The stage following the installation is ultrasound. The procedure is carried out to control the result, check the location of the spiral. The next visit to the gynecologist should take place no later than a month later. This period is enough for the body to react to a foreign object.
A woman who has decided to become a mother needs to remove the spiral. The same must be done when the period of validity of the device has expired (depending on the type, it may vary, but does not exceed the threshold of five years). Menstruation is the perfect time to get rid of an IUD. Removing the spiral in women, when the cervix is open, will save the process from unpleasant tactile sensations. Removal occurs through special threads that are part of the spiral. The next step is an ultrasound. The study will show if any individual elements remain inside the body.
Side effects of the intrauterine device
With a competent history of the patient, the absence of contraindications and the professional work of physicians, the introduction and removal of the spiral cannot in any way affect the risk of infertility, even if the spiral was removed ahead of schedule. Many women decide to abandon the IUD after the symbolic time of wearing it. The reason is painful heavy periods, in which you have to use painkillers in unacceptably large quantities. A hormonal spiral made of high-quality materials is able to get rid of such consequences, which does not negate the need to regularly monitor the consistency and duration of menstrual flow.
All possible Negative consequences spiral settings appear in the first months, after which they pass safely. If this does not happen, do not torture yourself, it is better to remove the spiral. The main consequences appear as:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- spotting that is not related to natural menstruation;
- prolonged painful menstruation;
- loss of the spiral during physical exertion or exercise in the gym.
There is a risk of pregnancy, which in these conditions will develop ectopic. Only the use of the hormonal spiral to the maximum eliminates this risk. At the same time, the hormonal device has a direct effect on endocrine system person. If the selected spiral does not belong to hormonal appearance, its installation can provoke excessive growth of the endometrium, the formation of fibroids.
The highest quality spirals created using advanced technologies may be contraindicated in patients who have experienced an ectopic pregnancy at the time of establishment, have a narrowed transition to the cervix, its altered shape (not corresponding to the norm), myoma.
Intrauterine contraceptives include devices that are inserted into the uterine cavity in order to prevent pregnancy - these are spirals and hormonal capsules. The most common intrauterine device (IUD). Intrauterine devices can be drug and non-drug. Medical models contain copper and silver and have a combined contraceptive action(Now only such IUDs are used). The spiral is a copper wire wrapped around an elastic rod 3-4 cm long, to which 2 nylon threads are attached. The spiral is inserted by the doctor into the uterine cavity. Once there, it prevents the onset of pregnancy due to the presence of a foreign body in the uterus and the spermicidal effect of copper. The spiral also enhances the contraction of the uterus and tubes, causing a special "aseptic" inflammation in the uterine cavity, which creates unfavorable conditions for the onset pregnancy.
Hormonal intrauterine contraceptives are various devices containing capsules with hormonal drugs, which are slowly released into the uterine cavity over 5 years. They render local action on the internal tissues of the uterus, fallopian tubes, cervical mucosa.
IUDs may be a suitable form of contraception for those of us who, for whatever reason, cannot take birth control pills. Spirals are recommended for women who are married and have a regular sex life. When using the spiral, one must have sex with a regular sexual partner, since the spiral makes the body particularly vulnerable to sexually transmitted diseases. The spiral can only be successfully applied if you are practically healthy, especially in terms of gynecology.
When should an intrauterine device not be used?
In order to successfully apply the coil, you must be gynecologically healthy. The coil can be inserted if you have not had a sexually transmitted disease within 10-12 months before.
Relative contraindications to the use of the spiral are: inflammatory diseases pelvic organs after the last pregnancy; previous ectopic pregnancies; blood clotting disorder; heart defects; chronic menstrual disorders, including very painful or heavy periods; high risk of sexually transmitted diseases; any disease that affects immune system or suppressing resistance to infections, such as diabetes or the use of corticosteroids.
Absolute contraindications to the use of the spiral: acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of the external and internal genital organs; confirmed or suspected pregnancy; uterine bleeding unknown origin; confirmed or suspected oncological disease genitals; pathological disease genitals; pathological changes in the uterus that prevent the successful insertion and effective use of the coil.
What examination should be done before the coil is inserted?
First of all, you need to make sure that you are not sick with an infectious and inflammatory disease. Therefore, the doctor is obliged to carefully ask the patient about her state of health, refer her to blood and urine tests, take special tissue samples and bacteriological smears. To determine the appropriate size and model of the spiral, you need to do ultrasound procedure uterus.
How and when is the spiral inserted?
This procedure is carried out only in medical institutions. Usually, the spiral is packed in sterile bags with special devices, which allows you to insert the spiral into the uterine cavity on the gynecological chair in 2-3 minutes. The cervix is pre-lubricated with a disinfectant and anesthetic raster. When introducing a spiral, sterility is of paramount importance. Most women tolerate this manipulation easily and painlessly. Some experience mild pain, lightheadedness and. Less commonly, the insertion of the coil is accompanied by short-term severe pain, which can cause fainting, nausea, etc. These feelings pass quickly. The best time to insert a spiral is the last days of menstruation, the first 6 weeks after childbirth, a spiral can also be inserted during a medical.
What complications can arise when using a spiral?
A frequent complication is the loss of the spiral from the uterine cavity. Most often this happens in the very first hours after the introduction of the spiral or in the first three months of its use. If the spiral remains in the uterus after this period, then experts say that it has “taken root”. In itself, the loss of the spiral is not dangerous, it is important to notice this in time and consult a doctor who will select a more appropriate size and model of the spiral.
During the first 3-8 months, your body "gets used" to the spiral. It is during this period that various complications can arise: inflammatory diseases of the genital organs are exacerbated, hidden infections urinary tract. Therefore, if symptoms such as itching and burning in the vagina, pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, fever, general malaise, chills appear, you should consult a doctor and begin treatment of the disease. Frequent complications with the introduction of the spiral are various uterine bleeding: from moderate spotting between menstruation to heavy debilitating bleeding during menstruation. In such cases, it is necessary to conduct individual treatment. If the bleeding becomes permanent and can be treated medicines, then it becomes necessary to remove the spiral. If the introduction of the spiral is extremely painful or very difficult, then this is a good reason to abandon the intrauterine contraceptive.
A very rare, but rather serious complication is a puncture of the uterus with a helix. Such cases occur on average in one woman out of five thousand, but still, if you decide to put yourself a spiral, you need to clearly imagine the spiral, what a uterine puncture is and what consequences it can entail. Most often, an organ puncture occurs when a spiral is inserted into the uterus or when it is tried to be removed. In this case, the patient is given emergency care, and there are practically no further complications.
It is much more dangerous when the puncture occurs under normal conditions of use of the helix. It is not yet possible to name with full certainty the reasons for which this is connected. Remember the main symptoms of a uterine puncture:
1. Pain in the abdomen, which can take on a very different character: from mild discomfort to acute severe pain. Pain may appear in the lumbar region, Bladder, pelvic area, etc.
2. General weakness, pallor, increased heart rate - these signs are symptoms of internal bleeding, which is accompanied by a puncture of the uterus or any other internal organ.
What are the benefits of a spiral? Spiral efficiency - 98%. The spiral is designed for long periods of use: from 2 to 5 years. After the introduction of the spiral, there is usually no need for special medical supervision. The spiral does not affect the entire body. The ability to conceive is restored within 1-2 menstrual cycles. Indicated for women over 35 and for those who are contraindicated in contraceptive pills. Spirals are affordable, the procedure for setting them does not take much time.
What are the disadvantages of a spiral? The use of a spiral is less effective than taking birth control pills. On average, 2-3 women out of 100 who use the spiral during the year become pregnant, despite the well-established spiral. The coil does not protect against contracting sexually transmitted diseases. There may be a complete or partial loss of the spiral, which can lead to an unplanned pregnancy.
What to do if pregnancy has occurred, and the spiral is in the uterus?
In half of the cases, a pregnancy that occurs against the background of the use of a spiral ends in a spontaneous miscarriage. In this case, the spiral may also fall out. If it remains inside, then it should be removed. In other cases, women who do not want to keep the pregnancy are done, during which the spiral is removed. It is more difficult to resolve the issue if a woman wants to have a baby. Domestic gynecologists advise to terminate such a pregnancy, Western doctors say that the fetus can be carried. An important point is the removal of the spiral. If she has retained the "antennae" and, therefore, is easily pulled out of the uterus, then pregnancy and childbirth proceed with virtually no complications associated with the use of the spiral. If the spiral remains in the uterus, then the pregnancy should proceed under the supervision of a doctor. The spiral does not negatively affect the fetus and the condition of the uterus, but can cause miscarriage in the second third of pregnancy.
Can the spiral damage the partner's organs during intercourse?
Even if the spiral falls out of the uterus during intercourse (which is practically not noted), then it cannot injure the penis, as it has a rounded and streamlined shape.
|
What are intrauterine contraceptives and how do they work? How to treat the disease? What are intrauterine contraceptives and how do they work? Folk methods of treatment and healing. Unique healing video sessions. |
If pill contraceptives worsen your well-being, and vaginal suppositories and condoms do not allow you to enjoy your sex life at 100%, you should try this method of preventing unwanted conception, such as intrauterine device (IUD).
Uterine spiral is a device made of plastic with the addition of copper, which is created taking into account the physiological characteristics and size of the uterine cavity.
Taking the right position inside the female organ, the copper parts of the IUD create a spermicidal effect and prevent the penetration of the egg into the uterine space.
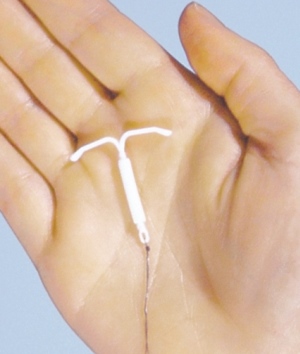
"In addition, the spiral blocks the growth of the endometrium, which makes the introduction of the egg into the uterus almost impossible, even if conception has occurred."
The advantages of intrauterine devices include the following:
1) high percentage of efficiency (from 95 to 99%);
2) long term use;
3) the minimum list of contraindications and adverse reactions;
4) immediate restoration of childbearing function after removal of this contraceptive from the uterus;
5) modern spirals do not cause discomfort in women, they are not felt at all inside the uterus;
6) the insertion and removal of the IUD is a simple, fast and painless procedure.
Types of intrauterine devices
The intrauterine device, the types of which your gynecologist can advise, must meet the individual requirements of your body and take into account its features. There are more than 50 varieties of intrauterine contraceptives, which are grouped into 3 main types.
1. Polymer coils of the first generation
This species can be called the "progenitor" of the modern uterine spiral. Such contraception was made from polymeric materials, and had side effects and low efficiency. That is why back in the 1990s, doctors switched to new types of contraceptive spirals.
2. Metal-containing intrauterine devices
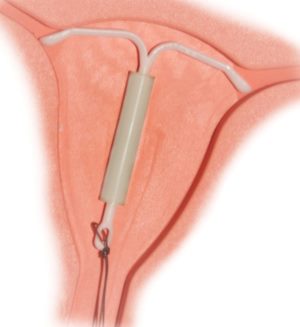
More modern look uterine contraceptives have become medical spirals with the addition of copper, silver or gold. Copper is considered the most effective metal due to its ability to react with uterine secretions and create an acidic environment. This spermicidal effect has made the second and third generation coils much more reliable than the previous versions.
3. Hormonal contraceptive coils
And, finally, the most modern type of intrauterine contraception - hormonal spirals. The principle of their action lies in the hormones that are contained in the leg of the spiral and dosed into the body for 5-7 years. This ensures reliable contraceptive effect 2 in 1.
"Price hormonal spirals much more expensive than previous analogues, but the high price is offset by efficiency and lack of negative impact on female organs. "
How to use an intrauterine device: instructions
When the decision on intrauterine contraception is made, your gynecologist will schedule the insertion of a helix on days 3-8 of the menstrual cycle. The risk of injuring the cervix is minimal during this period.
You need to pay attention to such important points before procedure:
1) make sure that you have no contraindications to the IUD;
2) get tested and undergo an ultrasound scan of the small pelvis;
How to put an intrauterine device
The process of insertion of the IUD takes no more than 15 minutes. The doctor measures the depth of the cervical canal, inserts a spiral and cuts off the antennae. After the procedure, the gynecologist may schedule an examination for you a few days later to make sure that the spiral is in a normal position.
Are negative consequences of the IUD possible?

IUDs are contraindicated for pregnant and nulliparous women, patients with pathologies of the pelvic organs, tumors, bleeding, etc. Properly selected uterine spirals practically do not cause negative consequences.
But non-compliance with the rules for the introduction and contraindications of the IUD can cause serious harm to women's health:
1) increased risk of ectopic pregnancy;
2) inflammatory processes female organs, endometriosis;
3) pain and spasms in the uterus;
4) infertility.
It is absolutely impossible to remove the spiral yourself. After the expiration of its validity, entrust this procedure to a specialist. Consider all the details and possible consequences Navy, and be healthy!
